Protecting the health of the athlete is one of the goals of the International Olympic Committee (IOC).1 The Olympic Movement Medical Code, which governs the actions of the IOC Medical Commission and sport organisations, also emphasises the importance of protecting the health of the athlete.2 In 2005, the IOC published the Consensus Statement (Consensus Statement) and the IOC Position Stand (Position Stand)3 on the Female Athlete Triad.4 Based on scientific evidence published in the intervening period, this Consensus Statement serves to update and replace these documents and provide guidelines to the athlete health support team to guide risk assessment, treatment and return-to-play decisions for affected athletes.
Relative energy deficiency in sport
In the 2005 IOC Consensus Statement,4 the Female Athlete Triad (Triad) was defined as ‘the combination of disordered eating (DE) and irregular menstrual cycles eventually leading to a decrease in endogenous oestrogen and other hormones, resulting in low bone mineral density’(BMD) based on the original scientific evidence of Drinkwater et al.5 In 2007, following progress in scientific understanding, the American College of Sports Medicine redefined the Triad as a clinical entity that refers to the ‘relationship between three inter-related components: energy availability (EA), menstrual function and bone health’. Added was an understanding of the pathophysiology describing the concept that over a period of time, the athlete moves along on a continuous spectrum ranging from the healthy athlete with optimal EA, regular menses and healthy bones to the opposite end of the spectrum characterised by amenorrhoea, low EA and osteoporosis.6
Since 2007, scientific evidence and clinical experience show that the aetiological factor underpinning the Triad is an energy deficiency relative to the balance between dietary energy intake (EI) and the energy expenditure required to support homoeostasis, health and the activities of daily living, growth and sporting activities. It is also evident that the clinical phenomenon is not a triad of three entities of EA, menstrual function and bone health, but rather a syndrome resulting from relative energy deficiency that affects many aspects of physiological function including metabolic rate, menstrual function, bone health, immunity, protein synthesis, cardiovascular and psychological health. In addition, it is evident that relative energy deficiency also affects men. Therefore, a new terminology is required to more accurately describe the clinical syndrome originally known as the Female Athlete Triad. Based on its interdisciplinary expertise, the IOC Consensus group introduces a more comprehensive, broader term for the overall syndrome, which includes what has so far been called the ‘Female Athlete Triad’: Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (RED-S).
The syndrome of RED-S refers to impaired physiological function including, but not limited to, metabolic rate, menstrual function, bone health, immunity, protein synthesis, cardiovascular health caused by relative energy deficiency.
The underlying problem of RED-S is an inadequacy of energy to support the range of body functions involved in optimal health and performance. EA is calculated as EI minus the energy cost of exercise relative to fat-free mass (FFM) and in healthy adults, a value of 45 kcal/kg FFM/day equates energy balance.7 Low EA, which occurs with a reduction in EI and/or increased exercise load, causes adjustments to body systems to reduce energy expenditure, leading to disruption of an array of hormonal, metabolic and functional characteristics.7 DE underpins a large proportion of cases of low EA, but other situations, such as a mismanaged programme to quickly reduce body mass/fat or an inability to track EI with an extreme exercise commitment, may occur without such a psychological overlay.7
Although the literature on low EA has focused on female athletes, it has also been reported to occur in male athletes.8 Prevalence studies of low EA in male athletes have been few, however, low EA appears to occur among the same at risk sports as for female athletes: the weight sensitive sports in which leanness and/or weight are important due to their role in performance, appearance or requirement to meet a competition weight category.8
Although simple messages about optimal, tolerable and unsafe levels of EA have been provided9 there are some caveats in the science. First, the complex dose–response relationship between reduction in EA and the disruption of various hormones10 and bone formation markers11 vary in nature and thresholds. Therefore, the cost of any energy mismatch should be carefully considered before it is implemented. A second caveat is that it is now known that the resting metabolic rate in athletes of small body size is underestimated in the linear scaling of EA relative to LBM/FFM.12 Finally, findings from laboratory settings may not apply as cleanly to free-living athletes. Numerous studies in female athletes have failed to find clear thresholds or associations between field determinations of low EA and objective measures of energy conservation such as metabolic hormones13 and menstrual disturbances.14 It is possible that other factors seen in free-living populations such as psychological stress, greater variability in between-day and within-day energy deficiency or dietary characteristics interact with each other to alter the effects of low EA.
Disordered eating
The disordered eating (DE) continuum starts with appropriate eating and exercise behaviours, including healthy dieting and the occasional use of more extreme weight loss methods such as short-term restrictive diets (<30 kcal/kg FFM/day).15 The continuum ends with clinical eating disorders (EDs), abnormal eating behaviours, distorted body image, weight fluctuations, medical complications and variable athletic performance. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) diagnostic classifications for EDs include anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, binge ED and other specified and unspecified feeding or ED.16These EDs have many features in common, and athletes frequently move among them.8 The pathogenesis of EDs is multifactorial with cultural, familial, individual and genetic/biochemical factors playing roles.17 In addition, factors specific to sport such as dieting to enhance performance, personality factors, pressure to lose weight, frequent weight cycling, early start of sport-specific training, overtraining, recurrent and non-healing injuries, inappropriate coaching behaviour and regulations in some sports have been suggested.8 The prevalence of DE is about 20% and 13% among adult and adolescent female elite athletes, and 8% and 3% in adult and adolescent male elite athletes, respectively.15 ,18 The prevalence differs significantly among sports.15
Hormonal and metabolic imbalance
Eumenorrhea is defined as regular cycles occurring at intervals between 21 and 35 days. In adolescents, the cycles range between 21 and 45 days.19 Primary amenorrhoea is defined as no menarche by age 15 years.20 Secondary amenorrhoea refers to an absence of three consecutive cycles post-menarche. Oligomenorrhea is defined as a cycle length greater than 45 days. Estimates of the prevalence of menstrual disorders in athletes vary widely.21 Secondary amenorrhoea prevalence is estimated in collegiate women from 2% to 5% and as high as 69% in dancers22 and 65% in long-distance runners.23 Primary amenorrhoea in collegiate athletes was found to be 7% overall, and was higher (22%) in cheerleading, diving and gymnastics.24 Subtle menstrual dysfunction, such as very light bleeding, mildly extended menstrual interval and premenstrual and postmenstrual spotting may occur, and may be underestimated by routine screening.25
Abnormal levels of hormones,26 LH pulsatility, inadequate body fat stores, low EA and exercise stress may be aetiological factors in menstrual disorders in athletes. Marked reduction in EA may disrupt the LH pulsatility by affecting the hypothalamic hormone gonadotropin-releasing hormone output27 which subsequently alters the menstrual cycle. This is known as Functional Hypothalamic Amenorrhea (FHA). Rapid or significant fat mass reduction, even over as short as a 1-month period, may compromise menstrual function. Low EA alters levels of metabolic hormones and substrates, for example, insulin, cortisol, growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), 3,3,5-triiodothyronine, grehlin, leptin, peptide tyrosine–tyrosine, glucose, fatty acids and ketones.28
Health and performance consequences of RED-S
RED-S can have serious implications for many body systems, resulting in short-term and long-term compromise of optimal health and performance. Athletes who suffer from long-term low EA may develop nutrient deficiencies (including anaemia), chronic fatigue and increased risk of infections and illnesses, all of which have the potential to harm health and performance.6Physiological and medical complications involve the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, endocrine, reproductive, skeletal, renal and central nervous systems.6 Psychological stress and/or depression can result in low EA and EDs and can also be a result of low EA.17Research indicates that muscle protein synthesis is reduced even at EA of 30 kcal/kg FFM/day.29 Low EA causes unfavourable lipid profiles and endothelial dysfunction, thereby increasing cardiovascular risk.30 Hormonal and metabolic abnormalities caused by RED-S and carbohydrate deficiency can result in a reduction in glucose utilisation, mobilisation of fat stores, slowing of metabolic rate and a decreased production of growth hormone.31
Irregular or absent menses may have significant emotional impact creating anxiety and an altered perception of self-normalcy.32 It may also confound conception, leading to unexpected pregnancy as well as inaccurate dating of pregnancy. Long-term reproductive repercussions of RED-S for women and men are unknown.
RED-S also has adverse health consequences for bone. Peak bone mass occurs around 19 years in women and 20.5 years in men.33 Oestrogen increases uptake of calcium into blood and deposition into bone, while progesterone facilitates the actions of oestrogen through multiple complex mechanisms.34 Even silent oestrogen/progesterone imbalance, as seen in subclinical ovulatory disturbances with low EA may produce negative changes in bone.35 In men and women, testosterone has anabolic effects on bone, stimulating osteoclasts and increasing bone formation and calcium absorption.36 Low-testosterone levels have been associated with low BMD in male athletes.37 Endogenous oestrogens and androgens have independent effects on bone development in both sexes.38 ,39 Increases in the stress hormones, catecholamines and cortisol, concomitant with low EA, have a negative effect.40 The bones of athletes with chronic amenorrhoea, benefit less from the osteogenic effects of exercise.41Although low BMD was first attributed to hypoestrogenism of menstrual dysfunction, low EA is now recognised as an independent factor of poor bone health at all levels of energy deficiency due to decreased IgF-1 and bone formation markers levels.42 Bone loss in these athletes may be irreversible.43
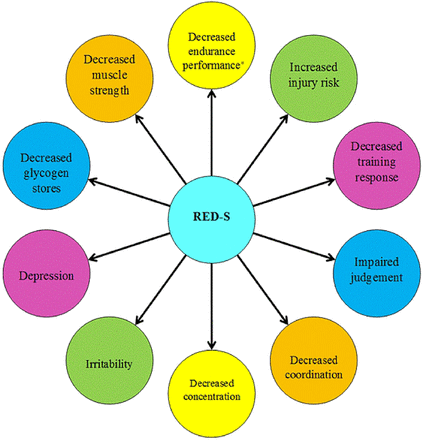
Changes in bone structure lead to an increased risk of stress fractures.44 Dietary insufficiencies increase the risk of stress fractures in both sexes.45 ,46 Additional risk factors include menstrual dysfunction,47 compulsive exercise, underlying poor bone health48 ,49low body mass index, prior fracture50 and eating psychopathology.49–51 High-risk stress fractures (ie, femoral neck) occur in adolescent athletes with the RED-S, and can have serious long-term consequences52 ,53 (figure 1). RED-S can also affect athletic performance. Functional impairments associated with low energy availability include a greater prevalence of viral illnesses,55injuries56 and most critically reduced responsiveness to training and subsequent performance.57 Further studies of performance effects of low energy availability are likely to provide significant incentive to change damaging behaviours. Such studies should confirm under which situations these effects occur (figure 2). In addition, some athletes with disordered eating/eating disorders practise extreme weight control methods (fasting, vomiting, diuretic and laxative abuse) that have possible health and performance consequences such as dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, and gastrointestinal problems, including esophagitis and oesophageal perforation from vomiting. Diuretics and some diet pills may contain WADA prohibited substances.58
Figure 1
Health Consequences of Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (RED-S) showing an expanded concept of the Female Athlete Triad to acknowledge a wider range of outcomes and the application to male athletes (*Psychological consequences can either precede RED-S or be the result of RED-S). Adapted from Constantini.54
Potential Performance Effects of Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (*Aerobic and anaerobic performance). Adapted from Constantini.54
Athletes of non-caucasian ethnicity
The prevalence of low EA has been studied mainly in females of Caucasian, European or European American descent. Whether race plays a role in the incidence and underlying aetiology of the RED-S remains speculative.
Race is a significant variable for several of the individual Triad components in non-athletic women. For example, a lower risk of ED is shown in African-American than Caucasian women,71 even among adolescent athletes.72 Whether the prevalence of menstrual disorders differs among racially diverse, athletic groups is currently unknown. In non-athletes, menarche occurs significantly earlier in African-American than in Caucasian or European American women.73 The BMD of African-American non-athletic females is significantly greater than that of Caucasian women, with a lower risk of osteoporosis and fracture.74 In athletes, little is known about the differences in BMD among ethnic groups, especially in the presence of low EA, DE/EDs and hormonal and metabolic imbalances. Stress fractures in African-American military recruits are lower than in Caucasian recruits.75 Based on preliminary data of a multicentre study, African-American and African black athletes exhibit similar symptoms of low EA, with Caucasian athletes showing greater risk of DE/EDs and menstrual dysfunction76 and no advantage for BMD in African black athletes.77 There are no published scientific studies in Hispanic and limited evidence on Asian athletes.78
Screening and diagnosis
Relative energy deficiency and EDs in sport
The screening and diagnosis of RED-S is challenging, as symptomatology can be subtle. A high index of suspicion of the athlete at risk is needed. Early detection is crucial to improve performance and prevent long-term health consequences. Screening for RED-S should be undertaken as part of an annual Periodic Health Examination (PHE) and when an athlete presents with DE/ED, weight loss, lack of normal growth and development, menstrual dysfunction, recurrent injuries and illnesses, decreased performance or mood changes. Although various screening instruments exist,16 ,82 ,83 they have not been validated and there is no consensus on which screening tool has the best efficacy.84 ,85 Furthermore, these tools exclude men, disabled athletes and are not ethnically diverse.
Since low EA plays a pivotal role in the development of the RED-S, diagnosis should focus on identification of the presence and causes of the low EA. Unfortunately, there are no standardised guidelines to determine EA. EA is equivalent to EI minus the cost of exercise energy expenditure (EEE) relative to FFM or lean body mass: EA (kcal/kg FFM/day) = (EI (kcal/day)−EEE (kcal/day )) The measurement of each of these components requires expertise and is generally imprecise. EI can be assessed by retrospective (recall) or prospective (written or electronic food diary) methods.86 EEE is usually assessed by an exercise log and tables of energy expenditure associated with sports/exercise activities, but may be supplemented where available by data collected via modern sports technology (eg, Global Positioning System Units, Heart Rate Monitors or Power Meters). Ideally, EI and EEE are measured over a similar time period that is representative of habitual practices. FFM can be quantified by methods such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) and anthropometry.87 A measurement of resting metabolic rate via indirect calorimetry may provide confirmation of suppressed metabolism secondary to low EA. Underpinning factors related to an unintentional mismatch between EI and large training/competition volume, intensity or misguided weight loss practices may be relatively easy to diagnose.
The Brief Eating Disorder in Athletes Questionnaire (BEDA-Q) is a validated screening tool that shows promising results in terms of distinguishing between female elite athletes with and without ED/DE.88 The Gold Standard for the diagnosis of EDs is the Eating Disorder Examination interview (EDE-16).89 For diagnostic criteria for ED see APA.16
Menstrual dysfunction
FHA is a diagnosis of exclusion. Assessment of irregular menses should include a menstrual history assessing age of menarche, regularity of menses, use of medications, the presence of other health issues and a family menstrual history. Physical examination includes assessment of anthropometry, pubertal stage, signs of ED and secondary causes of amenorrhoea.83 Pelvic examination may reveal pregnancy or hypoestrogen-related vaginal atrophy. Laboratory assessment of haemoglobin, luteinising hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, prolactin, oestradiol, T4, thyroid stimulating hormone, pregnancy and androgen profile may be indicated. More extensive testing might include a pelvic ultrasound and endometrial sampling to rule out other gynaecological pathologies.
Bone health
In athletes with low EA, DE, ED or amenorrhoea of over 6 months, BMD should be measured by DXA.90 ,91 In the adolescent, DXA should include the whole body (head excluded) in addition to the lumbar spine.6 ,92 As athletes in weight-bearing sports should have 5–15% higher BMD than non-athletes93 ,94 a BMD Z-score <−1.0 SD warrants further attention. In the athlete population, low BMD is defined as a Z-score between −1.0 and −2.0 SD, together with a history of nutritional deficiencies, hypoestrogenism, stress fracture or other secondary clinical risk factors for fracture. A value below −2.0 SD is considered as osteoporosis with the presence of secondary clinical risk factors.6 The recommended interval to reassess BMD via DXA scan for athletes at risk, or who are being treated for low BMD is 12 months in adults and a minimum of 6 months in adolescents.95
Treatment strategies of RED-S
Treatment strategies for low EA
The treatment of low EA should involve an increase in EI, reduction in exercise or a combination of both. The only strategy to have received scientific scrutiny is the addition of an energy-rich supplement (eg, liquid meal product) to habitual intake and a small reduction in, or introduction of a rest day to the weekly training programme.96–98 Despite the small sample size, this intervention was successful,96 ,97 however, not in all studies98 as this strategy may fail to address many underlying dietary and psychological factors. While developing a strategy to implement a diet of known and appropriate EA may be logical, it is usually impractical due to the challenges of measuring EA in the field. Therefore, a practical treatment approach to address low EA is to implement an eating plan that increases current EI by ∼300–600 kcal/day (1.2–2.4 MJ/day) and addresses suboptimal practices related to energy spread over the day and around exercise sessions, dietary composition and food-related stress.
Treatment strategies for low EA-associated menstrual dysfunction
In collegiate athletes, weight gain is the strongest predictor of recovery of normal menstrual function.99–101 Adequate protein and carbohydrate intake is recommended to restore liver glycogen to facilitate LH pulsatility.31 ,102 The time frame for the resumption of menses varies according to the severity of the energy deficiency and the duration of the menstrual dysfunction.100
Although oral contraceptives (OCs) may be considered for athletes requiring contraception,103 these may mask the low EA, menstrual dysfunction and perpetuate bone loss. Injectable depot medroxyprogesterone, another form of contraception, can cause amenorrhoea and hence prolonged use can adversely affect BMD,104 and adolescent bone mass accrual,105 which is reversible to a certain extent on discontinuation.106 Many physicians prescribe low-dose OCs as hormone replacement in the amenorrheic athlete, however, this intervention does not correct the aetiological cause of relative energy deficiency and may compromise the attainment of peak bone density.107
Treatment options to restore fertility may include increasing EA. Pharmacological agents may be necessary to stimulate ovulation in luteal phase deficiency.27 Attention must be paid to infertility treatments identified in the WADA Prohibited List.58
Treatment strategies to optimise bone health
Strategies to reverse bone loss in women with FHA parallel those used for amenorrheic women with anorexia.108 In the latter population, weight gain with or without the subsequent resumption of menses restores the coupling of bone formation and resporption109 ,110 and improves BMD.109 However, full recovery may not be feasible, as bone microarchitecture is also impaired.111 EI alone increases bone mass by 1–10% in women with anorexia.110 ,112 It is essential to restore the energy and oestrogen-dependent mechanisms of bone loss in order to improve mineralisation of trabecular bone and growth of cortical bone.41 Mechanical loading and high-impact sports are known to positively affect BMD113 ,114 as well as bone geometry.115 ,116Programmes of high-impact loading and resistance training should be implemented at least 2–3 days/week for athletes in non-weight bearing sports and/or those with decreased BMD.6
The athlete diet should include 1500 mg/day of calcium through dietary sources with supplementation if required.117 The Endocrine Society Guideline (2011) recommends maintaining vitamin D [25(OH)D] blood levels above 32–50 ng/mL, with 1500–2000 IU/day of vitamin D.118 ,119 Vitamin D deficiency is common in northern latitudes, especially during winter when there are fewer hours of sunlight and among athletes who train indoors.120 ,121 Other factors include dark pigmented skin, and the use of sunscreen. A recent meta-analysis of vitamin D supplementation found a positive effect in femoral and hip BMD, with no effect in the spine.122
Transdermal oestradiol (given with cyclic progesterone) has shown some success in increasing BMD in patients with anorexia.123 In some studies, combination OCs containing 20–35 µg of oestradiol have maintained or improved BMD in amenorrheic athletes.124,125 However, use of the OCP in athletes with FHA have been reported to have a detrimental effect on BMD through the suppression of androgen secretion and cause premature closure of the epiphyses compromising growth of the long bones in adolescents.126
Bisphosphonates, which inhibit the resorption of bone, are not recommended for women of reproductive age, as they are stored in bone for prolonged amounts of time and have been shown to be teratogenic.127 ,128 Other therapies including raloxifene (a selective oestrogen receptor modulator or SERM), parathyroid hormone peptides, teriperatide and calcitonin, are also not approved for use in premenopausal women. Some novel potential therapies are being developed, but clinical trials are lacking.129,130 These include insulin-derived growth factor (a bone anabolic agent)131 ,132 and leptin which can be used to stimulate appetite, thus effecting resumption of menses and subsequent improvement in BMD.133–135
In men, detection and correction of any underlying pathology is essential, including testosterone therapy with hypogonadism and osteoporosis. Bisphosphonates may be used as monotherapy, as consolidative therapy after a course of teriperatide administration or in combination with hormonal replacement.136 Denusomab and strontium ranelate also increase BMD in men with osteoporosis.137
Treatment strategies for psychological sequelae
If an athlete will not or cannot follow the treatment plan, a psychological factor is generally present. Athlete resistance to treatment usually increases with the severity of the eating problem.138 Treatment should be provided by a mental health professional knowledgeable about the management of EDs in athletes. The frequency, types, intensity and duration of psychological treatment depend on the severity, chronicity and the medical and psychological complications of the eating problem, as well as the comorbid psychological disorders that often accompany such problems. Ideally, eating problems can be treated on an outpatient basis. Medical complications, risk of self-harm and lack of progress in outpatient treatment indicate a need for more intensive treatment regimens including inpatient, residential, partial hospitalisation and intensive outpatient programmes. Treatment is usually required for several months. Treatment modalities might include cognitive behavioural therapy, dialectical behaviour therapy or family-based therapy. Comorbid conditions, such as depression, anxiety and other psychological problems also need to be addressed. Pharmacotherapy may also be recommended; antidepressants are the class of medications most often prescribed.139